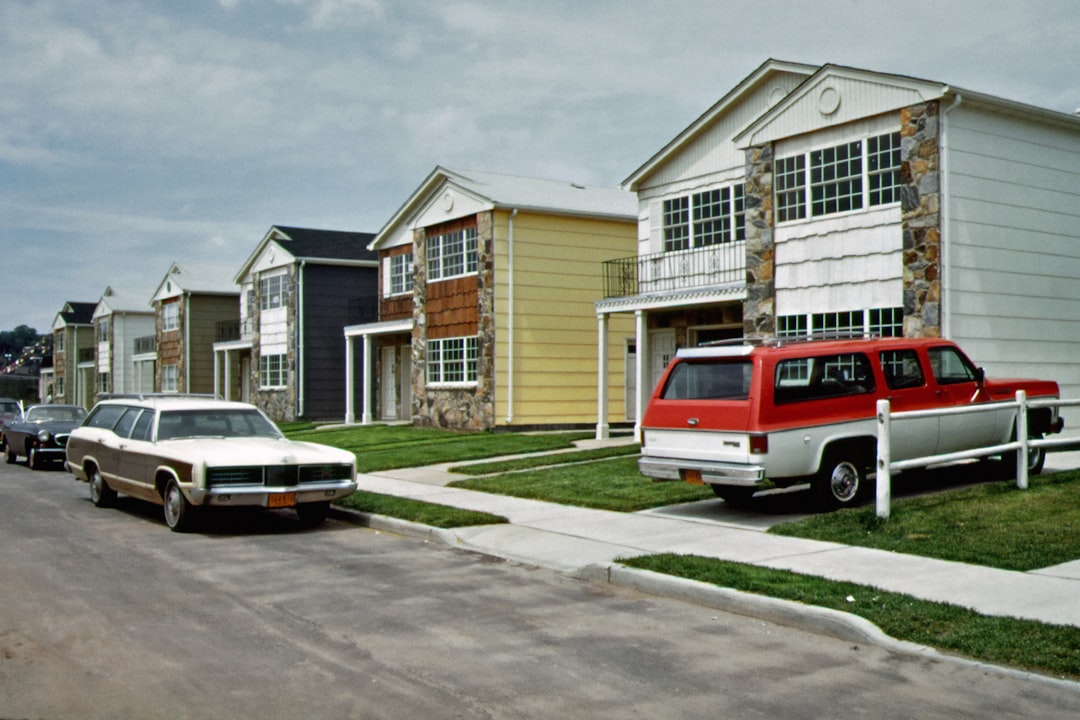
The concept of modular prefab homes can be traced back to the early 20th century, a time when industrialization was reshaping the landscape of construction. The first significant movement towards prefabricated housing emerged during World War II, when there was an urgent need for quick and efficient housing solutions for returning soldiers and their families. The U.S. government initiated programs to produce affordable homes rapidly, leading to the development of standardized building components that could be manufactured in factories and assembled on-site. This marked a pivotal moment in the history of housing, as it introduced the idea of mass production to residential construction. As the decades progressed, modular homes evolved significantly. The post-war boom saw a surge in suburban development, and companies began to refine their techniques for producing modular components. By the 1960s and 1970s, modular homes were becoming more sophisticated, with improved designs and materials that allowed for greater customization. The introduction of new technologies, such as computer-aided design (CAD), further revolutionized the industry, enabling architects and builders to create more complex and aesthetically pleasing structures. This evolution laid the groundwork for the modern modular home, which combines efficiency with a variety of design options.
Key Takeaways
- Modular prefab homes have a rich history rooted in efficient, factory-built construction methods.
- They offer advantages like faster build times, quality control, and reduced on-site disruption.
- These homes provide significant environmental benefits through less waste and energy-efficient designs.
- Modular prefab homes are cost-effective, often saving money compared to traditional building methods.
- They allow for diverse design and customization options to meet various homeowner preferences.
The Advantages of Modular Prefab Homes
One of the most significant advantages of modular prefab homes is their speed of construction. Unlike traditional homes that can take months or even years to complete, modular homes can be built in a fraction of that time. The construction process typically takes place in a controlled factory environment, where components are manufactured simultaneously while site preparation occurs.
This parallel approach not only accelerates the overall timeline but also minimizes delays caused by weather or other external factors. As a result, homeowners can move into their new residences much sooner than they would with conventional building methods. In addition to speed, modular homes offer remarkable quality control.
Since they are constructed in a factory setting, builders can implement stringent quality assurance measures at every stage of production. This controlled environment reduces the likelihood of defects and ensures that each component meets high standards before it is transported to the building site. Furthermore, many modular homes are built to meet or exceed local building codes, providing homeowners with peace of mind regarding safety and durability.
This focus on quality is a compelling reason for many buyers to consider modular options over traditional construction.
The Environmental Benefits of Modular Prefab Homes
Modular prefab homes are increasingly recognized for their environmental benefits, which stem from both their construction methods and energy-efficient designs. One of the primary advantages is the reduction of waste generated during the building process. In a factory setting, materials can be cut and assembled with precision, minimizing off-cuts and excess materials that often end up in landfills during traditional construction.
Additionally, many manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices by sourcing eco-friendly materials and utilizing renewable energy sources in their factories. Energy efficiency is another critical aspect of modular homes that contributes to their environmental appeal. Many modern modular designs incorporate advanced insulation techniques, energy-efficient windows, and sustainable heating and cooling systems.
These features not only reduce the carbon footprint of the home but also lead to lower utility bills for homeowners. For instance, some modular homes are designed to meet or exceed Energy Star certification standards, ensuring that they consume less energy over their lifespan compared to conventional homes. As awareness of climate change grows, the demand for environmentally friendly housing solutions like modular prefab homes continues to rise.
The Cost-Effectiveness of Modular Prefab Homes
| Metric | Traditional Homes | Modular Prefab Homes | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Construction Time | 8-12 months | 3-6 months | Modular homes are built faster due to factory assembly |
| Average Cost per Square Foot | 150-200 | 100-150 | Lower labor and material waste reduce costs |
| Labor Costs | High | Moderate | Factory setting reduces on-site labor needs |
| Material Waste | 15-20% | 5-10% | Controlled factory environment minimizes waste |
| Energy Efficiency | Standard | High | Better insulation and sealing in prefab modules |
| Customization Options | High | Moderate | Modular designs may have some limitations |
| Financing Availability | Widely Available | Increasingly Available | Growing acceptance of prefab homes by lenders |
| Resale Value | Standard | Comparable | Market acceptance improving for modular homes |
Cost-effectiveness is a significant factor driving interest in modular prefab homes. The streamlined construction process allows builders to save on labor costs, which can be substantial in traditional homebuilding scenarios. Since much of the work is completed in a factory setting, there is less reliance on skilled labor at the construction site, where labor costs can fluctuate based on demand and availability.
This efficiency translates into lower overall costs for consumers, making homeownership more accessible for many individuals and families. Moreover, modular homes often come with predictable pricing structures. Buyers can receive detailed estimates upfront, which helps them avoid unexpected expenses that frequently arise during traditional construction projects.
This transparency is particularly appealing to first-time homebuyers who may be navigating the complexities of financing and budgeting for a new home. Additionally, the long-term savings associated with energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs further enhance the financial attractiveness of modular prefab homes.
The Design and Customization Options for Modular Prefab Homes
One common misconception about modular prefab homes is that they lack design flexibility; however, this could not be further from the truth. Modern modular homes offer an impressive array of design and customization options that cater to diverse tastes and preferences. Homebuyers can choose from various floor plans, exterior finishes, and interior layouts to create a space that reflects their unique style.
Many manufacturers provide extensive catalogs showcasing different designs, allowing buyers to visualize their future homes before making decisions. Furthermore, advancements in technology have enabled greater customization capabilities than ever before. With computer-aided design tools, architects can create bespoke designs tailored to individual needs while still adhering to modular construction principles.
Homeowners can opt for features such as open-concept living spaces, energy-efficient appliances, and smart home technology integration. This level of personalization ensures that each modular home is not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing and aligned with the homeowner’s lifestyle.
The Construction Process of Modular Prefab Homes
The construction process for modular prefab homes is distinct from traditional building methods in several key ways. Initially, the process begins with site preparation, which includes clearing land and laying foundations. While this groundwork is being completed, the actual modules are constructed simultaneously in a factory setting.
This dual approach significantly reduces the overall timeline for completion. Once the modules are built—typically consisting of walls, floors, and roofs—they are transported to the site using specialized trucks. Upon arrival, cranes are employed to lift each module into place on the foundation.
The modules are then connected through a series of structural and utility connections, including plumbing, electrical wiring, and HVAC systems. This assembly process is often completed within days rather than weeks or months, allowing homeowners to see their vision come to life rapidly.
The Popularity and Demand for Modular Prefab Homes
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in interest in modular prefab homes across various demographics. Factors contributing to this trend include rising housing costs in urban areas, increased awareness of environmental issues, and a growing desire for efficient living solutions. As more individuals seek affordable housing options without compromising quality or design, modular homes have emerged as an attractive alternative.
The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated this demand as people reassessed their living situations and sought more flexible housing solutions. With remote work becoming more prevalent, many individuals began looking for homes that could accommodate home offices or multi-functional spaces. Modular homes offer versatility in design that aligns well with these evolving needs.
Additionally, as younger generations prioritize sustainability and affordability in their housing choices, manufacturers are responding by creating innovative designs that appeal to these values.
The Future of Modular Prefab Homes
Looking ahead, the future of modular prefab homes appears promising as technology continues to advance and societal needs evolve. Innovations such as 3D printing and advanced robotics are beginning to play a role in the construction process, potentially further reducing costs and construction times while enhancing design capabilities. These technologies could enable even greater customization options while maintaining efficiency.
Moreover, as urbanization continues to rise globally, there will likely be an increasing demand for affordable housing solutions that can be deployed quickly in densely populated areas. Modular prefab homes are well-suited to meet this challenge due to their adaptability and speed of construction. As cities grapple with housing shortages and rising costs, policymakers may also begin to recognize the potential of modular housing as a viable solution to address these pressing issues.
In conclusion, as awareness grows regarding the benefits of modular prefab homes—ranging from environmental sustainability to cost-effectiveness—their popularity is expected to continue rising in both urban and rural settings alike. With ongoing innovations in design and construction methods, these homes will likely play an essential role in shaping the future landscape of residential living.



